264x Filetype PDF File size 1.22 MB Source: irimee.indianrailways.gov.in
RADIOGRAPHY
OBJECTIVES
To:
• understand the principle of radiographic
testing methods
• Know the technique of testing
• Become familiar with standards & codes
• Learn the applications.
INTRODUCTION
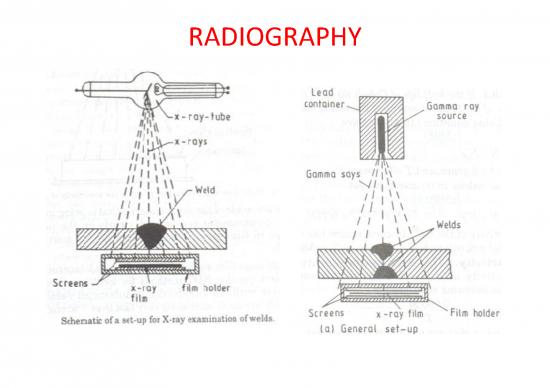
Radiography:
• one of the oldest & the most widely used NDT which
uses X-rays or -rays radiation to examine the interior
of the materials.
• gives a permanent film record of defects that is easy
to interpret.
• applied for assessing the quality of the welded joints
also.
• can detect flaws or discontinuities in welds such as
cracks, porosity & blow holes, slag, flux or oxide
inclusions, lack of fusion between the weld metal &
the parent metal, incomplete penetration, tungsten
inclusion, etc.
PROPERTIES OF X- RAYS & - RAYS
X- rays are highly penetrating electromagnetic
radiations of wave length shorter than UV-rays (X-
rays: 5 to 0.0004A, - rays: 0.1 to 0.005A)
These rays have the following properties:
• Invisible electromagnetic radiations.
• Can penetrate matter. Penetration is less if density of
matter is more and thickness is more
• Are differentially absorbed.
• Travel in straight lines.
• Produce photochemical effects on films.
• May be refracted, reflected and diffracted
• Damage living tissues
• Ionise gases through which it pass.
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.