244x Filetype PDF File size 2.88 MB Source: www.scu.edu.au
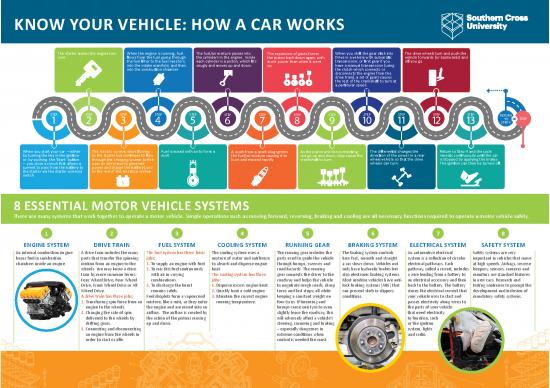
KNOW YOUR VEHICLE: HOW A CAR WORKS
The starter makes the engine turn When the engine is running, fuel The fuel/air mixture passes into The expansion of gases forces When you shift the gear stick into The drive wheels turn and push the
over. flows from the fuel pump through the cylinders in the engine. Inside the piston back down again, with Drive in a vehicle with automatic vehicle forwards (or backwards) and
the fuel filter to the fuel injectors, each cylinder is a piston, which fits more power than when it went transmission, or first gear if you off you go.
into the intake manifold, and then snugly and moves up and down. up. have a manual transmission (using
into the combustion chamber. the clutch which connects or
disconnects the engine from the
drive train), a set of gears causes
the rest of the crankshaft to turn at
a particular speed.
STEP STEP STEP STEP STEP STEP STEP STEP STEP STEP STEP STEP STEP RETURN
TO OR STOP
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 STEP 4
When you start your car – either The electric current stops flowing Fuel is mixed with air to form a A spark from a spark plug ignites As the piston and the connecting The differential changes the Return to Step 4 and the cycle
by turning the key in the ignition to the starter but continues to flow mist. the fuel/air mixture causing it to rod go up and down, they cause the direction of the power in a rear repeats continuously until the car
or by pushing the ‘Start’ button through the charging system (which burn and expand rapidly. crankshaft to turn. wheel vehicle so that the drive is stopped by applying the brakes.
– you close a circuit that allows a uses an alternator to generate wheels can turn. The ignition can then be turned off.
current to pass from the battery to power and charge the battery) and
the starter via the starter solenoid to the rest of the electrical system.
switch.
8 ESSENTIAL MOTOR VEHICLE SYSTEMS
There are many systems that work together to operate a motor vehicle. Simple operations such as moving forward, reversing, braking and cooling are all necessary functions required to operate a motor vehicle safely.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
ENGINE SYSTEM DRIVE TRAIN FUEL SYSTEM COOLING SYSTEM RUNNING GEAR BRAKING SYSTEM ELECTRICAL SYSTEM SAFETY SYSTEM
An internal combustion engine A drive train includes the many The fuel system has three basic The cooling system uses a The running gear includes the The braking system controls An automotive electrical Safety systems are very
burns fuel in combustion parts that transfer the spinning jobs: mixture of water and antifreeze parts used to guide the vehicle how fast, smooth and straight system is a collection of circular important in vehicles that move
chambers inside an engine. motion from an engine to the 1. To supply an engine with fuel. to absorb and disperse engine through bumps, swerves and a car slows down. Vehicles not electrical pathways. Each at high speeds. Airbags, reverse
wheels. You may know a drive 2. To mix this fuel continuously heat. road hazards. The running only have hydraulic brakes but pathway, called a circuit, includes beepers, sensors, cameras and
train by more common terms: with air in varying The cooling system has three gear connects the driver to the also electronic braking systems. a wire leading from a battery to monitors are standard features
Four Wheel Drive, Rear Wheel combinations. jobs: roadway and helps the vehicle Most modern vehicles have anti- an electrical accessory and then in new cars. Research and
Drive, Front Wheel Drive or All 3. To discharge the burnt 1. Disperse excess engine heat. to negotiate rough roads, sharp lock braking systems (ABS) that back to the battery. The battery testing continues to prompt the
Wheel Drive. remains safely. 2. Quickly heat a cold engine. turns and fast stops; all while can prevent skids in slippery stores the electrical current that development and inclusion of
A drive train has three jobs: Fuel droplets form a vapourised 3. Maintain the correct engine keeping a constant weight on conditions. your vehicle uses to start and mandatory safety systems.
1. Transferring spin force from an mixture, like a mist, as they enter running temperature. four tyres. If bouncing and passes electricity along wires to
engine to the wheels. the engine and are mixed into an bumps cause one tyre to even the parts of your vehicle
2. Changing the rate of spin airflow. The airflow is created by slightly leave the roadway, this that need electricity
delivered to the wheels by the action of the pistons moving will adversely affect a vehicle’s to function, such
shifting gears. up and down. steering, cornering and braking as the ignition
3. Connecting and disconnecting – especially dangerous in system, lights
an engine from the wheels in extreme conditions when and radio.
order to start or idle. control is needed the most.
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.