330x Filetype PPTX File size 0.25 MB Source: www.umich.edu
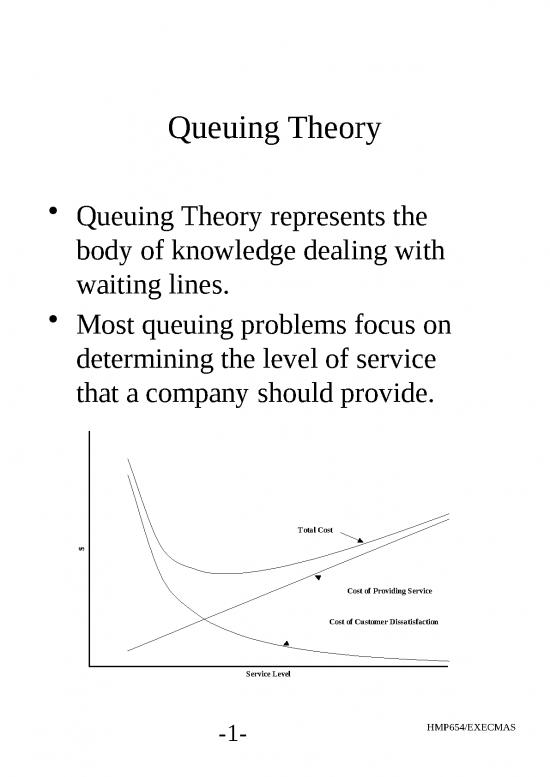
Queuing Theory
Queuing Systems Configurations
Customer Customer
Arrives Leaves
Waiting Line Server
Customer
Leaves
Server 1
Customer Customer
Arrives Leaves
Waiting Line Server 2
Customer
Leaves
Server 3
Customer Customer
Arrives Server 1 Leaves
Waiting Line
Customer Customer
Arrives Leaves
Waiting Line Server 2
Customer Customer
Arrives Leaves
Waiting Line Server 3
-2- HMP654/EXECMAS
Queuing Theory
Characteristics of a Queuing Process
• Generation of Customers
–Infinite vs. Finite calling
population
–Homogeneity of the calling
population
–Individual vs. Batch arrivals
–Deterministic vs. Stochastic
arrivals
• Queuing of Customers
–Single vs. Multiple servers
–Finite vs. Infinite queues
-3- HMP654/EXECMAS
Queuing Theory
Characteristics of a Queuing Process
–FIFO vs. LIFO disciplines
–Priority rules
• Servicing the Customers
–Deterministic vs. Stochastic
service time
–Individual vs. Batch Processing
-4- HMP654/EXECMAS
Queuing Theory
Characteristics of a Queuing Process
• Generation of Customers
–Poisson probability distribution
xe
p(x)
x!
‘x’ represents the number of arrivals
in a specific time period.
‘’ represents the ‘arrival rate’, that
is, the average number of arrivals
per time period.
-5- HMP654/EXECMAS
Queuing Theory
Arrival Rate
The time between arrivals is known as
the interarrival time. If the number
of arrivals in a given period follows
a Poisson distribution, with mean ,
the interarrival times follow an
exponential probability distribution
with mean 1/
The exponential distribution exhibit the
memoryless property. An arrival
process is memoryless if the time
until the next arrival occurs does not
depend on how much time has
elapsed since the last arrival.
-6- HMP654/EXECMAS
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.