|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
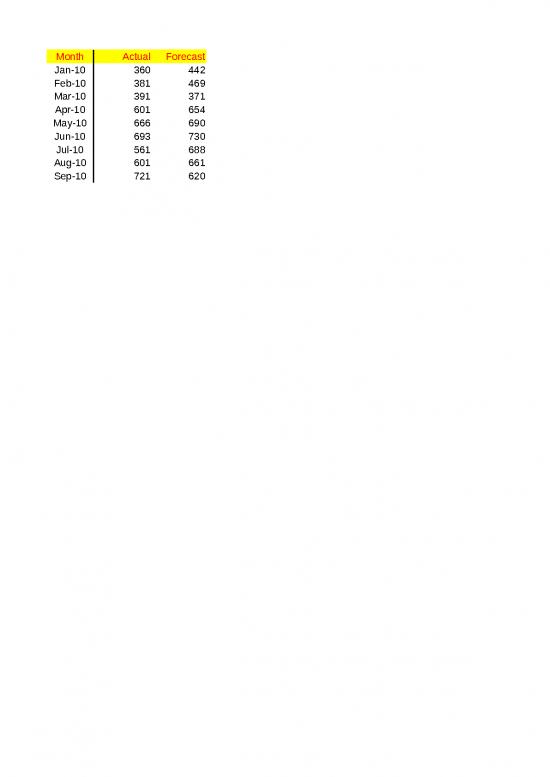
| Month |
Actual Demand Quantity |
Forecasted Demand |
Mchockalingam:
Error is with reference to the forecast. Deviation is with reference to the Average of the actual demand.
Forecast Error |
Absolute Deviation (from Mean Demand) |
Mchockalingam:
Deviation is with reference to the mean of the actual demand.
Cumulative Absolute Deviation |
Cumulative Forecast Error |
Absolute Forecast Error |
Cumulative Abs Forecast. Error |
Relative Absolute Error |
Mchockalingam:
Mean Absolute Deviation or
MAD (from Forecasted quantity) used in calculating tracking signal.
Running Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD) |
Signed % Error |
Absolute % Error |
Mchockalingam:
calculating deviation of actual values in consecutive periods
Delta between subsequent Demand Observations |
Mchockalingam:
Tracking signal = Σ (actual − forecast) / MAD
Tracking signal |
Mchockalingam:
Used to calculate Root Mean Square Error
Forecast Error Squared
Error^2 |
Mchockalingam:
Used to calculate R-Square
Squared Deviation from the Mean
(Deviation)^2 |
Mchockalingam:
Used to calculate Durbin-Watson
Error Auto-correlation:
[(Error at T) - (Error at (T-1)]^2 |
|
|
Mark Chockalingam:
The small letters indicate column indexes.
a |
b |
c |
d |
e |
f |
g |
h |
i |
j |
k |
l |
m |
n |
o |
p |
q |
r |
|
| Formula |
|
|
(b-c) |
|
cumulative (e) |
cumulative (d) |
absolute (d) |
Cumulative (h) |
i/f |
Running Mean of (h) |
d/b |
h/b |
|
(cumulative (d)/k) |
(b-c)^2 |
|
|
|
| Jan-10 |
360 |
442 |
-82.00 |
192.78 |
192.78 |
-82.00 |
82 |
82.00 |
0.43 |
82.00 |
-23% |
23% |
|
-1.00 |
6,724 |
37,163 |
|
|
| Feb-10 |
381 |
469 |
-88.00 |
171.78 |
364.56 |
-170.00 |
88 |
170.00 |
0.47 |
85.00 |
-23% |
23% |
21 |
-2.00 |
7,744 |
29,508 |
36 |
|
| Mar-10 |
391 |
371 |
20.00 |
161.78 |
526.33 |
-150.00 |
20 |
190.00 |
0.36 |
63.33 |
5% |
5% |
10 |
-2.37 |
400 |
26,172 |
11,664 |
|
| Apr-10 |
601 |
654 |
-53.00 |
48.22 |
574.56 |
-203.00 |
53 |
243.00 |
0.42 |
60.75 |
-9% |
9% |
210 |
-3.34 |
2,809 |
2,325 |
5,329 |
|
| May-10 |
666 |
690 |
-24.00 |
113.22 |
687.78 |
-227.00 |
24 |
267.00 |
0.39 |
53.40 |
-4% |
4% |
65 |
-4.25 |
576 |
12,819 |
841 |
|
| Jun-10 |
693 |
730 |
-37.00 |
140.22 |
828.00 |
-264.00 |
37 |
304.00 |
0.37 |
50.67 |
-5% |
5% |
27 |
-5.21 |
1,369 |
19,662 |
169 |
|
| Jul-10 |
561 |
688 |
-127.00 |
8.22 |
836.22 |
-391.00 |
127 |
431.00 |
0.52 |
61.57 |
-23% |
23% |
132 |
-6.35 |
16,129 |
68 |
8,100 |
|
| Aug-10 |
601 |
661 |
-60.00 |
48.22 |
884.44 |
-451.00 |
60 |
491.00 |
0.56 |
61.38 |
-10% |
10% |
40 |
-7.35 |
3,600 |
2,325 |
4,489 |
|
| Sep-10 |
721 |
620 |
101.00 |
168.22 |
1052.67 |
-350.00 |
101 |
592.00 |
0.56 |
65.78 |
14% |
14% |
120 |
-5.32 |
10,201 |
28,299 |
25,921 |
|
| Total |
4975.00 |
5325.00 |
-350.00 |
1052.67 |
|
|
592.00 |
|
|
|
-77% |
115% |
625.00 |
|
49,552 |
158,342 |
56,549 |
|
| Average |
552.78 |
591.67 |
Author:
Forecast Bias
-38.89 |
Author:
Mean Absolute Deviation or MAD (from Average Demand)
116.96 |
|
|
Author:
Mean Absolute Error or
Average absolute Forecast Error
65.78 |
|
|
|
Mchockalingam:
Mean percent Error - Not a recommended method since extremely small values will heavily influence this calculation.
Recommended method is to use the Forecast Bias.
-9% |
13% |
78.13 |
|
Mchockalingam:
Mean Square Error
5,506 |
17,594 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mchockalingam:
MASE: Mean Absolute Scaled Error
Formula=MAD/MAD attained on Historical sales
MASE does not have an intuitive explanation and not widely adopted.
MASE |
0.84 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sr. No. |
Forecast Metrics |
Value |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
Number of Observations |
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
Arithmetic Mean of Actual Demand |
552.78 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
Mchockalingam:
Also called Mean Absolute Error
Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD) |
65.78 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
Standard Deviation |
140.69 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
Coefficient of Variation |
25% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
Mean Percent Error (MPE) |
-9% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
Mean Absolute Percent Error ( MAPE) |
13% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
Forecast Bias |
-7.04% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
Mchockalingam:
formula= MAD/MEAN, also called as WMAPE; Weighted Mean Absolute Percent Error
Weighted Absolute Percent Error (WMAPE) |
11.90% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
MAD-Mean Ratio |
11.90% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
Forecasting Efficiency Quotient |
53.25% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
R-Square |
0.69 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
Mean Squared Error (MSE) |
5,506 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) |
74.20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
Median Absolute Percent Error (MdAPE) |
10% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
Tracking Signal |
-5.32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
Mchockalingam:
Geometric Mean of Relative Absolute Error
Geometric Mean of Relative Absolute Error (GMRAE) |
0.45 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
Durbin-Watson |
1.14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
Mean Absolute Scaled Error |
0.84 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|