196x Filetype PDF File size 0.07 MB Source: www.macollege.in
V SEMSTER ZOOLOGY
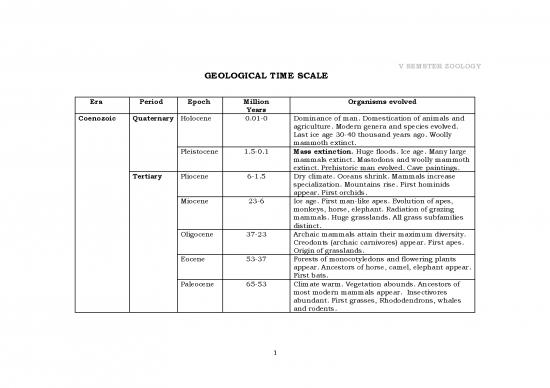
GEOLOGICAL TIME SCALE
Era Period Epoch Million Organisms evolved
Years
Coenozoic Quaternary Holocene 0.01-0 Dominance of man. Domestication of animals and
agriculture. Modern genera and species evolved.
Last ice age 30-40 thousand years ago. Woolly
mammoth extinct.
Pleistocene 1.5-0.1 Mass extinction. Huge floods. Ice age. Many large
mammals extinct. Mastodons and woolly mammoth
extinct. Prehistoric man evolved. Cave paintings.
Tertiary Pliocene 6-1.5 Dry climate. Oceans shrink. Mammals increase
specialization. Mountains rise. First hominids
appear. First orchids.
Miocene 23-6 Ice age. First man-like apes. Evolution of apes,
monkeys, horse, elephant. Radiation of grazing
mammals. Huge grasslands. All grass subfamilies
distinct.
Oligocene 37-23 Archaic mammals attain their maximum diversity.
Creodonts (archaic carnivores) appear. First apes.
Origin of grasslands.
Eocene 53-37 Forests of monocotyledons and flowering plants
appear. Ancestors of horse, camel, elephant appear.
First bats.
Paleocene 65-53 Climate warm. Vegetation abounds. Ancestors of
most modern mammals appear. Insectivores
abundant. First grasses, Rhododendrons, whales
and rodents.
1
Mesozoic Cretaceous Mass extinction. 60% of tetrapod families extinct.
135-65 Himalayas, Andes, Alps arise. Dinosaurs and
Ammonites extinct. First monocotyledons. First
marsupials and placental mammals (Pantotheres).
First flowering plants. Climate cool. Angiosperms
radiate.
Jurassic 205-135 First bird, Archaeopteryx. Dominance of dinosaurs.
Earliest mammals. Dicotyledons and conifers
common. Continents become high. Origin of insect
pollinators.
Triassic 250-205 Mass extinction. 80% of tetrapod families extinct.
Continental drift begins. Arid conditions.
Gymnosperms dominate. First dinosaurs. Mammal-
like reptiles. First teleosts, first crocodiles and first
flying reptiles.
Palaeozoic Permian 290-250 Mass extinction. 70% of tetrapod families extinct.
Single land mass, Pangaea and single ocean.
Continents rise. Glaciations set in. Expansion of
reptiles, origin of Cotylosauria and Therapsida. Last
trilobites.
Carbonife- Pennsylva- 290 Warm and humid climate. Swamps abundant. First
rous nian modern soils. First reptiles. Sharks abundant. First
mammal-like reptiles. Earthworms.
Mississipp- Forests of ferns and gymnosperms. Foraminiferans
ian 350 and shell-crushing sharks abound. First winged
insects. Radiation of amphibians. Little seasonal
variations.
Devonian 410-350 Mass extinction. Arid climate. First gymnosperm
forests. First amphibians (Labyrinthodonts). First
spiders. Dominance of fishes. First ferns. First
vascular plants. First insects.
Silurian 440-410 Algae dominate. Land plants definite. Trilobites
decline. First scorpions and millipedes appear. First
fishes, ostracoderms and placoderms appear.
2
Ordovician 510-438 Land submerged. Warm climate. Algae abound.
Plants invade land. First corals. First vertebrates.
Cephalopods and snails. First Agnatha.
Cambrian 600-510 Mass extinction. Mild climate. Marine algae. Many
invertebrates. Trilobites. Brachiopods. Sponges.
Molluscs. Explosion after mass extinction.
Proterozoic 3,500-600 Primitive aquatic algae and fungi. Annelid burrows.
Protozoa. Oxygenation of atmosphere. Prokaryote
radiation. Skeleton of sponges.
Archeozoic 4,600-3,500 Calcareous deposits by algae. Origin of life. Fossils
of cyanobacteria.
Solar 5,000-4,600 Formation of Solar system. Strong solar wind.
Formation of primitive atmosphere on earth.
Cosmic 20,000-5,000 Big Bang and matter synthesis.
3
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.