287x Filetype PDF File size 1.14 MB Source: isaacnewtonacademy.org
AQA GCSE Chemistry (Separate Science) Unit 1 Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table Higher Revision Activity Mat 1
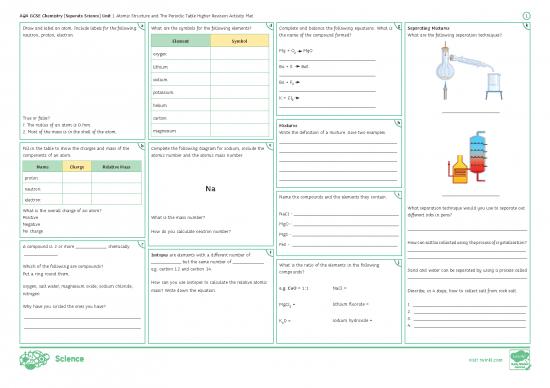
Draw and label an atom. Include labels for the following: a What are the symbols for the following elements? d Complete and balance the following equations. What is g Separating Mixtures k
neutron, proton, electron. the name of the compound formed? What are the following separation techniques?
Element Symbol
Mg + O MgO
oxygen 2
lithium Be + S BeS
sodium Be + F
2
potassium
K + Cl
2
helium
True or false? carbon h
1. The radius of an atom is 0.1nm Mixtures
2. Most of the mass is in the shell of the atom. magnesium Write the definition of a mixture. Give two examples.
Fill in the table to show the charges and mass of the b Complete the following diagram for sodium, include the e
components of an atom. atomic number and the atomic mass number.
Name Charge Relative Mass
proton
neutron Na
Name the compounds and the elements they contain. i
electron
What is the overall charge of an atom? What separation technique would you use to separate out
Positive What is the mass number? NaCl - different inks in pens?
Negative MgO -
No charge How do you calculate neutron number?
MgS -
A compound is 2 or more , chemically c FeS - How can salt be collected using the process of crystallisation?
. f
Isotopes are elements with a different number of
Which of the following are compounds? but the same number of , What is the ratio of the elements in the following j
e.g. carbon 12 and carbon 14. compounds? Sand and water can be separated by using a process called
Put a ring round them.
oxygen, salt water, magnesium oxide, sodium chloride, How can you use isotopes to calculate the relative atomic
mass? Write down the equation. e.g. CaO = 1:1 NaCl = Describe, in 4 steps, how to collect salt from rock salt.
nitrogen
MgCl = lithium fluoride = 1.
Why have you circled the ones you have? 2
2.
K 0 = sodium hydroxide = 3.
2 4.
visit twinkl.com
AQA GCSE Chemistry (Separate Science) Unit 1 Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table Higher Revision Activity Mat 2
Complete the electronic structure diagrams for: a List 3 halogens d Complete the following dot and cross diagrams for: g Describe the plum pudding model of the atom. j
oxygen , , , NaCl Draw a diagram.
How many electrons do they have in their outer shell?
Describe how the reactivity changes as you go down the
group.
magnesium
MgO
Write balanced symbol equations for the following reactions:
Why did scientists believe this model?
bromine + potassium iodide
Describe why the noble gases are so unreactive. b k
chlorine + sodium iodide Describe what the alpha scattering experiment showed
scientists.
fluorine + potassium chloride
The boiling points of the noble gases increase/decrease as e h
you go down the group. (delete the wrong answer) Can you Underline the properties of metals and circle the Complete word equations for the following reactions:
explain your answer? properties of non-metals:
sodium + chlorine
Strong, low density, malleable, dull, good conductors
of heat and electricity, high melting and boiling point, lithium + iodine
brittle, not good conductors of electricity.
potassium + bromine
Describe what happens to the reactivity of the alkali c James Chadwick discovered the… f
metals as you go down the group. (underline the correct answer) How are the groups arranged in the periodic table? i Niels Bohr discovered that l
proton
Why?
neutron
How can you tell that the alkali metals are very reactive? Why did Mendeleev leave gaps in the periodic table?
electron
Complete the word and symbol equation for sodium
reacting with water:
sodium + water sodium hydroxide + How can you tell the noble gases are unreactive? What happened to some of the gaps he left?
Na + NaOH +
visit twinkl.com
AQA GCSE Chemistry (Separate Science) Unit 1 Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table Higher Revision Activity Mat 3
The transition elements are a group of metals with similar properties which are different to the metals in group 1. a
Shade in the transition metals on the periodic table below.
Name three common transition metals. b Complete the sentences below to describe the properties c
of transition metals.
They form compounds when reacting.
They are of heat and electricity. They
are malleable. They have densities.
Compared to the alkali metals, they are reactive.
Complete the table to show the ions and colours formed by iron compounds. iron (III) oxide d
Compound Name Ion Colour
+
iron (II) hydroxide Fe²
+
Fe³
iron (III) oxide
visit twinkl.com
AQA GCSE Chemistry (Separate Science) Unit 1 Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table Higher Revision Activity Mat Answers 1
Draw and label an atom. Include labels for the following: a What are the symbols for the following elements? d Complete and balance the following equations. What is g Separating Mixtures k
neutron, proton, electron. the name of the compound formed? What are the following separation techniques?
Element Symbol
oxygen O 2Mg + O2 2MgO
magnesium oxide
lithium Li Be + S BeS
beryllium sulphide
sodium Na Be + F BeF
electrons 2 2
neutrons potassium K beryllium fluoride
protons 2K + Cl 2KCl
2
helium He potassium chloride
True or false? Distillation
1. The radius of an atom is 0.1nm True carbon C h
2. Most of the mass is in the shell of the atom. False, most Mixtures
of the mass is in the centre magnesium Mg Write the definition of a mixture. Give two examples.
Two or more elements together, not chemically joined and
Fill in the table to show the charges and mass of the b Complete the following diagram for sodium, include the e
components of an atom. atomic number and the atomic mass number. can be easily separated.
Name Charge Relative Mass Salt water, sand and water
proton +1 1 23 mass number
neutron 0 1 Na
Name the compounds and the elements they contain. i
electron -1 very small 11 atomic number Fractional distillation
What is the overall charge of an atom? NaCl - sodium chloride, sodium and chlorine What separation technique would you use to separate out
No charge What is the mass number? different inks in pens?
Total number of protons and neutrons. MgO - magnesium oxide, magnesium and oxygen
How do you calculate neutron number? MgS - magnesium sulfide, magnesium and sulfur Chromatography
Atomic mass – proton number
A compound is 2 or more elements, chemically joined. c FeS - iron sufide, iron and sulfur
f How can salt be collected using the process of crystallisation?
Which of the following are compounds? Isotopes are elements with a different number of By heating up a mixture of salt and water, the water will
Put a ring round them. neutrons but the same number of protons, e.g. carbon What is the ratio of the elements in the following j evaporate and leave the salt in the bowl.
12 and carbon 14. compounds?
oxygen, salt water, magnesium oxide, sodium chloride, Sand and water can be separated by using a process called
nitrogen How can you use isotopes to calculate the relative atomic filtration.
mass? Write down the equation. e.g. CaO = 1:1 NaCl = 1:1
Why have you circled the ones you have? sum of (isotope abundance x isotope mass number) Describe, in 4 steps, how to collect salt from rock salt.
Ar = MgCl = 1:2 lithium fluoride = 1:1 1. Grind the mixture;
They have 2 or more elements in the word equation. sum of abundances of all the isotopes. 2
2. Add water and stir;
K 0 = 2:1 sodium hydroxide = 1:1:1 3. Filter the mixture;
2 4. Evaporate the salt water and salt is left over.
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.