294x Filetype PDF File size 1.46 MB Source: www.gunt.de
REFRIGERATION THERMODYNAMICS OF THE REFRIGERATION CYCLE
BASIC KNOWLEDGE
THERMODYNAMICS OF THE REFRIGERATION CYCLE
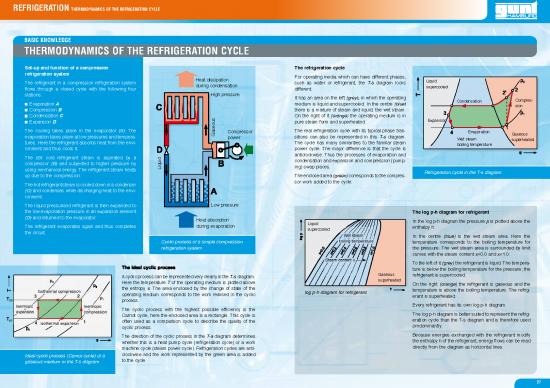
Set-up and function of a compression The refrigeration cycle
refrigeration system For operating media which can have different phases,
The refrigerant in a compression refrigeration system Heat dissipation such as water or refrigerant, the T-ss diagram looks Liquid
flows through a closed cycle with the following four during condensation different. supercooled
stations: Highg pressure It has an area on the left (grey), in which the operating
Evaporation A medium is liquid and supercooled. In the centre (blue) Condensation Compres-
Compression B there is a mixture of steam and liquid, the wet steam. sion
Condensation C s On the right of it (orange) the operating medium is in Expansionnnn
Expansion D ou pure steam form and superheated.
The cooling takes place in the evaporator (A). The se Compressor The real refrigeration cycle with its typical phase tran- Evaporation Gaseous
evaporation takes place at low pressures and tempera- Ga power sitions can also be represented in this T-ss diagram. Wet steam superheated
tures. Here the refrigerant absorbs heat from the envi- The cycle has many similarities to the familiar steam boiling temperature
ronment and thus cools it. power cycle. The major difference is that the cycle is
The still cold refrigerant steam is aspirated by a d anticlockwise. Thus the processes of evaporation and
compressor (B) and subjected to higher pressure by condensation and expansion and compression (pump-
using mechanical energy. The refrigerant steam heats Liqui ing) swap places.
up due to the compression. The enclosed area (green)corresponds to the compres- Refrigeration cycle in the T-s diagram
The hot refrigerant steam is cooled down in a condenser sor work added to the cycle.
(C) and condenses while discharging heat to the envi-
ronment.
The liquid pressurised refrigerant is then expanded to LLow pressure
the low evaporation pressure in an expansion element The log p-h diagram for refrigerant
(D) and returned to the evaporator. Heat absorption In the log p-h diagram the pressure pp is plotted above the
The refrigerant evaporates again and thus completes during evaporation Liquid enthalpy h.
the circuit. supercooled
In the centre (blue) is the wet steam area. Here the
Cyclic process of a simple compression boiling temperaturegp temperature corresponds to the boiling temperature for
refrigeration system the pressure. The wet steam area is surrounded by limit
curves with the steam content x=0.0 and x=1.0.
Steam contentttx To the left of it (grey) the refrigerant is liquid. The tempera-
ture is below the boiling temperature for the pressure; the
A cyclic process can be represented very clearly in the T-ss diagram. Gaseous refrigerant is supercooled.
Here the temperature TT of the operating medium is plotted above superheated On the right (orange) the refrigerant is gaseous and the
Isothermal compression the entropy s. The area enclosed by the change of state of the log p-h diagram for refrigerant temperature is above the boiling temperature. The refrig-
operating medium corresponds to the work realised in the cyclic erant is superheated.
process. Every refrigerant has its own log p-h diagram.
The cyclic process with the highest possible efficiency is the The log p-h diagram is better suited to represent the refrig-
Carnot cycle, here the enclosed area is a rectangle. This cycle is eration cycle than the T-s diagram and is therefore used
Isothermal expansionp often used as a comparison cycle to describe the quality of the predominantly.
cyclic process.
The direction of the cyclic process in the T-ss diagram determines Because energies exchanged with the refrigerant modify
whether this is a heat pump cycle (refrigeration cycle) or a work the enthalpy h of the refrigerant, energy flows can be read
machine cycle (steam power cycle). Refrigeration cycles are anti- directly from the diagram as horizontal lines.
Ideal cyclic process (Carnot cycle) of a clockwise and the work represented by the green area is added
gaseous medium in the T-s diagram to the cycle.
27
REFRIGERATION THERMODYNAMICS OF THE REFRIGERATION CYCLE
BASIC KNOWLEDGE
THERMODYNAMICS OF THE REFRIGERATION CYCLE
The refrigeration cycle in the log p-h diagram The refrigerant
The real refrigeration cycle consists of the following changes of state: Every cyclic process requires an operating medium which The different refrigerants are marked with an RR followed
in the refrigeration cycle is the refrigerant. In the refrigera- by a number.
1 – 2 polytropic compression on the tion cycle the refrigerant has the purpose of transporting The water often used in technical cycles is not suitable for
condensation pressure (for comparison heat. Here the high absorption of energy during evapora- the refrigeration cycle. At the low temperatures prevail-
1 – 2’ isentropic compression) tion or discharge of energy during the condensation of ing in a refrigeration system the evaporation pressure is
a liquid is utilised. To achieve this at the temperatures extremely low and there is a risk of the water freezing.
2 – 2’’ isobaric cooling, deheating of the prevailing in a refrigeration system at well manageable
pressures, liquids with a low boiling point, such as differ- The use of CO is technically demanding. Due to its low
superheated steam 2
ent fluorocarbons (FC), ammonia (NH3), carbon dioxide boiling temperature a very high pressure level results.
(CO ) or hydrocarbons such as butane or propane, are This means that common components from refrigera-
2’’ – 3’ isobaric condensation 2
used as operating medium. tion technology, such as valves, compressors or heat
3’ – 3 isobaric cooling, supercooling of the exchangers, cannot be used.
For NH there are also special components, because
liquid Boiling 3
Name temperature materials containing copper are not resistant against
3 – 4 isenthalpic expansion to the ammonia.
evaporation pressure FC R134a Pure substance Ts = -26°C
FC R404a Mixture Ts = -47℃
4 – 1’ isobaric evaporation FC R407a Mixture Ts = -39...-45°C
NH R717 Pure substance Ts = -33°C
1’ – 1 isobaric heating, superheating of the 3
steam The refrigeration cycle in the log p-h diagram Isobutane R600a Pure substance Ts = -12℃
CO R744 Pure substance Ts = -78°C
In addition there are also pressure losses in the real refrigeration cycle, which means that evaporation and condensation 2
are not exactly horizontal (isobaric).
Energy considerations in the log p-h diagram Important for a good operation is the steam pressure
The horizontal distances of the key cycle points in the curve of the operating medium. It should be gaseous
log p-h diagram correspond to the enthalpy differences. In the C at low pressures and at the desired cooling tempera-
simple refrigeration cycle without branched off mass flows these tures and liquid at high pressures and temperatures.
result in the energy flows or capacities of the ideal system when The pressure levels should also be easy to manage
multiplied with the refrigerant mass flow. The distances in the technically.
log p-h diagram are therefore a direct measure for the energy The diagram shows the steam pressure curve of the
flows exchanged. emperature in °
The distance 4 – 1 corresponds to the cooling capacity and is the T well suited FC R134a. Typical freezing temperatures
net capacity of the refrigeration system. The distance 1 – 2 is the of -26°C in the evaporator can be implemented with
drive power exerted via the compressor. The distance 2 – 3 corre- pressures around 1bar while for condensing only a
sponds to the heat capacity discharged via the condenser. This is pressure of 17bar at 60°C is required.
the waste heat of the refrigeration system. Pressure in bar a While in pure substances, such as NH , propane and
Steam pressure curve of FC R134a 3
CO , the steam pressure curve is fixed, it can be
From the ratio of the net capacity and the drive power the coef- 2,
ficient of performance COP can be calculated. adapted in FC within wide boundaries to meet require-
ments by mixing different base grades.
Energy flows in the refrigeration cycle h - h
COP = 1 4
cooling capacity absorbed h2 - h1
compressor drive power The coefficient of performance can be compared to the efficiency
heat capacity discharged in a work machine.
29
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.