249x Filetype PDF File size 0.14 MB Source: ubccriticalcaremedicine.ca
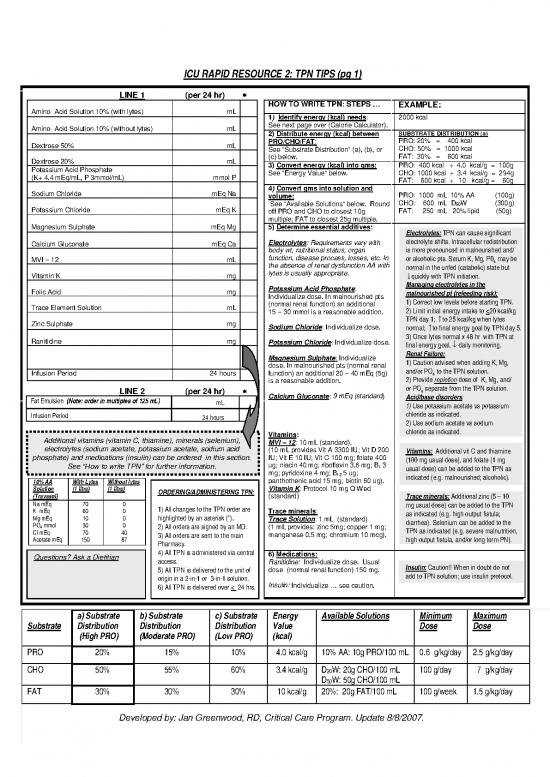
ICU RAPID RESOURCE 2: TPN TIPS (pg 1)
LINE 1 (per 24 hr) *
HOW TO WRITE TPN: STEPS … EXAMPLE:
Amino Acid Solution 10% (with lytes) mL 1 Identify energy (kcal) needs
) : 2000 kcal
Amino Acid Solution 10% (without lytes) mL See next page over (Calorie Calculator).
2) Distribute energy (kcal) between SUBSTRATE DISTRIBUTION (a)
Dextrose 50% mL PRO/CHO/FAT: PRO: 20% = 400 kcal
See “Substrate Distribution” (a), (b), or CHO: 50% = 1000 kcal
. FAT: 30% = 600 kcal
Dextrose 20% mL (c) below
Potassium Acid Phosphate 3) Convert energy (kcal) into gms: PRO: 400 kcal ÷ 4.0 kcal/g = 100g
(K+ 4.4 mEq/mL, P 3mmol/mL) mmol P See “Energy Value” below. CHO: 1000 kcal ÷ 3.4 kcal/g = 294g
FAT: 600 kcal ÷ 10 kcal/g = 60g
4 Convert gms into solution and
Sodium Chloride mEq Na ) PRO: 1000 mL 10% AA (100g)
volume:
CHO: 600 mL D W (300g)
Potassium Chloride mEq K See “Available Solutions” below. Round 50
off PRO and CHO to closest 10g FAT: 250 mL 20% lipid (50g)
multiple; FAT to closest 25g multiple.
Magnesium Sulphate mEq Mg 5) Determine essential additives: Electrolytes: TPN can cause significant
: Requirements vary with electrolyte shifts. Intracellular redistribution
Calcium Gluconate mEq Ca Electrolytes
body wt, nutritional status, organ is more pronounced in malnourished and/
MVI – 12 mL function, disease process, losses, etc. In or alcoholic pts. Serum K, Mg, P0 may be
the absence of renal dysfunction AA with 4
lytes is usually appropriate. normal in the unfed (catabolic) state but
Vitamin K mg ↓quickly with TPN initiation.
Potassium Acid Phosphate: Managing electrolytes in the
Folic Acid mg Individualize dose. In malnourished pts malnourished pt (refeeding risk):
(normal renal function) an additional 1) Correct low levels before starting TPN.
Trace Element Solution mL 15 – 30 mmol is a reasonable addition. 2) Limit initial energy intake to <20 kcal/kg
TPN day 1; ↑to 25 kcal/kg when lytes
Zinc Sulphate mg : Individualize dose.
Sodium Chloride normal; ↑to final energy goal by TPN day 5.
Ranitidine mg 3) Once lytes normal x 48 hr with TPN at
Potassium Chloride: Individualize dose. final energy goal, ↓ daily monitoring.
Renal Failure:
Magnesium Sulphate: Individualize 1) Caution advised when adding K, Mg,
dose. In malnourished pts (normal renal and/or PO to the TPN solution.
Infusion Period 24 hours function) an additional 20 – 40 mEq (5g) 4
is a reasonable addition. 2) Provide repletion dose of K, Mg, and/
or PO separate from the TPN solution.
LINE 2 (per 24 hr) * 9 mEq (standard 4
Calcium Gluconate: ) Acid/base disorders:
Fat Emulsion (Note: order in multiples of 125 mL) mL 1) Use potassium acetate vs potassium
Infusion Period chloride as indicated.
24 hours 2) Use sodium acetate vs sodium
chloride as indicated.
Vitamins:
Additional vitamins (vitamin C, thiamine), minerals (selenium),
: 10 mL (standard).
electrolytes (sodium acetate, potassium acetate, sodium acid MVI – 12
(10 mL provides Vit A 3300 IU; Vit D 200 Vitamins: Additional vit C and thiamine
phosphate) and medications (insulin) can be ordered in this section. IU; Vit E 10 IU; Vit C 100 mg; folate 400 (100 mg usual dose), and folate (1 mg
ug; niacin 40 mg; riboflavin 3.6 mg; B 3
See “How to write TPN” for further information. 1 usual dose) can be added to the TPN as
mg; pyridoxine 4 mg; B 5 ug;
12 indicated (e.g. malnourished; alcoholic).
10% AA With Lytes Without lytes panthothenic acid 15 mg; biotin 60 ug).
: Protocol 10 mg Q Wed
Solution (1 litre) (1 litre) ORDERING/ADMINISTERING TPN: Vitamin K
(Travasol) (standard) Trace minerals: Additional zinc (5 – 10
Na mEq 70 0 1) All changes to the TPN order are mg usual dose) can be added to the TPN
K mEq 60 0 Trace minerals
: as indicated (e.g. high output fistula;
Mg mEq 10 0 highlighted by an asterisk (*). : 1 mL (standard)
PO mmol 30 0 Trace Solution diarrhea). Selenium can be added to the
4 2) All orders are signed by an MD. (1 mL provides: zinc 5mg; copper 1 mg; TPN as indicated (e.g. severe malnutrition,
Cl mEq 70 40 3) All orders are sent to the main manganese 0.5 mg; chromium 10 mcg).
Acetate mEq 150 87 Pharmacy. high output fistula, and/or long term PN).
4) All TPN is administered via central 6) Medications:
Questions? Ask a Dietitian access. Ranitidine: Individualize dose. Usual
5) All TPN is delivered to the unit of dose (normal renal function) 150 mg. Insulin: Caution!! When in doubt do not
origin in a 2-in-1 or 3-in-1 solution. add to TPN solution; use insulin protocol.
6) All TPN is delivered over < 24 hrs. Insulin: Individualize … see caution.
a) Substrate b) Substrate c) Substrate Energy Available Solutions Minimum Maximum
Substrate Distribution Distribution Distribution Value Dose Dose
(High PRO) (Moderate PRO) (Low PRO) (kcal)
PRO 20% 15% 10% 4.0 kcal/g 10% AA: 10g PRO/100 mL 0.6 g/kg/day 2.5 g/kg/day
CHO 50% 55% 60% 3.4 kcal/g D W: 20g CHO/100 mL 100 g/day 7 g/kg/day
20
D W: 50g CHO/100 mL
50
FAT 30% 30% 30% 10 kcal/g 20%: 20g FAT/100 mL 100 g/week 1.5 g/kg/day
Developed by: Jan Greenwood, RD, Critical Care Program. Update 8/8/2007.
ICU RAPID RESOURCE 2: TPN TIPS (pg 2)
DETERMINING ENERGY REQUIREMENTS: CALORIE CALCULATOR GI COMPLICATIONS: IDENTIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT
PREVENTION
COMPLICATION POSSIBLE SYMPTOMS TREATMENT
TABLE 1 HOW TO USE TABLE ETIOLOGY
Fatty liver • Excess kcal kcal • Avoid over
↑ •↓
• liver
AGE SEX STRESS ENERGY Step # 1: Refer to Table 1; select patient age and gender. (hepatic • Unbalanced enzymes • Provide feeding
LEVEL (Kcal) Step # 2: Go to Table 2; identify appropriate stress level. steatosis) TPN (excess within 1- 3 cyclic TPN • Provide
Step # 3: Return to Table 1; read across to the CHO) weeks of TPN (deliver over balanced TPN
18 - 25 M Mild 2150 corresponding goal energy requirement. • Chronic initiation < 24 h) • Avoid CHO
Mod 2300 infections • Rule out all >7 g/kg/day
High 2650 Step # 4: Table 1 based on weight of 60 - 65 kg for ♀ and possible • Early EN
70 – 75 kg for ♂. Refer to Table 3 to modify energy (kcal) for causes
F Mild 1700 • Transition
Mod 1850 patients who do not fall within this weight range. to EN/oral
High 2150 intake ASAP
26 -35 M Mild 2050 Note! In significantly malnourished pts, the initial
Mod 2200 Cholestasis Precise serum alk kcal Avoid
High 2600 energy goal (kcal) should not exceed 20 kcal/kg. • •↑ •↓ •
Refer to section 5 (pg over) “Managing electrolytes etiology phosphatase • Rule out overfeeding
F Mild 1650 unknown • Progressive other causes • Early EN
Mod 1800 in the malnourished pt”. (? impaired bile ↑ serum • Transition
High 2100 flow; lack of bilirubin to EN/oral
TABLE 2 TABLE 3 intraluminal • Jaundice feedings
36 -50 M Mild 1950 stimulation of ASAP
Mod 2100 STRESS EXAMPLES - BODY WEIGHT ADJUST hepatic bile
High 2400 LEVEL CLINICAL MASS (Kg) ENERGY secretion;
CONDITION excess
F Mild 1600 VERY F <40
250 kcal substrate).
Mod 1700 overdose −
High 2000 NONE - stroke SMALL M <55
MILD
GI atrophy • Lack of • Bacterial • Transition • Early EN
51 -70 M Mild 1800 <10% burn-injury SMALL F 40 - 55 125 kcal
Mod 1950 − enteric translocation to enteral/oral
mild infection M 55 - 65 stimulation Æ feedings
High 2250 minor elective surgery villous atrophy ASAP
LARGE F 70 - 80 125 kcal
F Mild 1450 MOD 10 - 20% burn-injury +
Mod 1550 M 80 – 100
High 1850 significant surgery
VERY F >80 250 kcal
moderate pancreatitis +
71 -90 M Mild 1650 >20% burn-injury LARGE M >100 ADDITIONAL RESOURCES:
Mod 1800 HIGH severe infection ASPEN board of directors guidelines for the use of parenteral
High 2050 Obese pts: use corrected wt.
major surgery (ABW –IBW) x 0.25 + IBW and enteral nutrition in adult and pediatric patients. JPEN 2002;
F Mild 1400 multiple trauma 26(1): 1SA – 137SA
Mod 1500 severe pancreatitis
High 1750 severe CHI Calorie Calculator developed Mirtallo J, et al. Safe practices for parenteral nutrition. JPEN 2004;
by: J. Greenwood, RD. 28:S39-S70
METABOLIC COMPLICATIONS: IDENTIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT
COMPLICATION POSSIBLE SYMPTOMS TREATMENT PREVENTION COMPLICATION POSSIBLE SYMPTOMS TREATMENT PREVENTION
ETIOLOGY ETIOLOGY
Hyperglycemia • Rapid infusion CHO • BG > 11 mmol/L • Initiate insulin • Slow initiation and Hyponatremia • Excessive fluid intake • Edema • Restrict fluid intake • Avoid over hydration
Dilutional states Wt gain Na intake if • Provide 40-60 mEq/day
solution • •↓ advancement of CHO • • •↑
Metabolic CHO in TPN (CHF, SIADH) • Muscle weakness deficient per 1000 kcal unless
• Diabetes acidosis especially pts with DM • Excessive Na loss • CNS dysfunction contraindicated
• Sepsis/infection • Provide balanced TPN (vomiting, diarrhea) (irritability, apathy, • Monitor fluid status
• Steroids confusion, seizure)
• Pancreatitis Hypermagnesemia Respiratory Mg in TPN Monitor serum levels
Hypoglycemia • Excessive Mg • •↓ •
• Abrupt TPN • Weakness • Administer CHO • Taper TPN and/or provide intake paralysis
termination • Sweating CHO from alternate source • Renal insufficiency • Hypotension
• Insulin overdose • Palpitations (tube feed, oral intake) • Premature
• Lethargy • Monitor BG after TPN ventricular contracts
• Shallow termination • Lethargy
respirations • Cardiac arrest
Hypomagnesemia Cardiac Mg supplementation
Hyperkalemia •↓ • •↓ • • Refeeding • • • Provide 8-20 mEq Mg per
renal function Diarrhea K intake Monitor serum levels. malnourished pt arrhythmias kcal/CHO in TPN day
• Excessive K intake • Tachycardia • Provide K binder • Correct acid-base disorder •↓
• Hemolysis • Cardiac arrest • If metabolic • Assess for drug nutrient • Alcoholism • Tetany • Slow initiation and
• Metabolic acidosis • Paresthesia acidosis change interactions (i.e. K sparing • Diuretics use • Convulsions advancement of TPN (esp.
loss (diarrhea) • Muscular CHO) in malnourished and
• K sparing drugs potassium and diuretics) •↑ or alcoholic pts
sodium chloride to • Drugs (cyclosporin) weakness
acetate alternative • DKA • Monitor serum levels
Hyperphosphatemia Excessive PO Parethesia PO in TPN Monitor serum levels
Hypokalemia • Inadequate K • Nausea •↑ • per • 4 • •↓ 4 •
K in TPN Provide 1-2 mEq/kg K administration • Flaccid paralysis
intake • Vomiting • Correct acid – day (unless contraindicated) • Renal dysfunction • Mental confusion
•↑ •
loss (diarrhea, • Confusion base disturbance Slow initiation of TPN • Hypertension
NG loss, diuretics) • Arrhythmias • Discontinue NG (especially CHO) in • Cardiac
• Refeeding • Cardiac arrest suction if possible malnourished and/or arrhythmias
malnourished pt • Respiratory • Resolve diarrhea alcoholic pt • Tissue calcification
• Low Mg •↓
depression kcal/CHO in Hypophosphatemia Refeeding Respiratory failure PO in TPN Monitor serum levels
• Metabolic alkalosis TPN • • •↑ 4 •
• Paralytic ileus malnourished pt • Cardiac kcal/CHO in TPN • Provide 20 – 40 mmol
•↓
• Steroids • Alcoholism abnormalities PO per day.
4
loss (diarrhea, • CNS dysfunction Initiate TPN (especially
•↑ •
Hypernatremia • Inadequate free • Thirst •↑ • large NG loss) • Difficulty weaning CHO) slowly in
free water Provide optimal free water DKA from ventilator malnourished pts
water •↓ intake • •
skin turgor Avoid excess Na Hypertriglyceridemia Excessive lipid Serum TG > 4.0 TPN lipid Pre TPN: assess for pre-
• Excessive Na intake •↓ • • •↓ •
•↑ Na intake •
serum Na, Monitor fluid status Sepsis mmol/L infusion time existing hx of TG
• Excessive water urea, hematocrit • • ↑ ↑
loss • Meds (cyclosporine) • Limit lipid to <1 g/kg/day
Prerenal azotemia Dehydration Elevated serum fluid intake • Monitor serum urea
• • •↑
Excess PRO intake urea PRO load
• •↓
nonprotein kcal
•↑
Reviewed by: Dr. Dean Chittock, MD, Elena Tejedor, RD, members of the ICU QA/QI Committee
and members of the Nutrition Practice Council (2006).
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.